Structured Data : Though rarely understood, structured data is frequently mentioned. However, if you want your website to rank highly in most search engines, you must have a fundamental understanding of what structured data is, why it matters, and how it may boost your SEO.
We will cover the fundamental ideas of structured data as well as the use of structured data for search engine optimisation in this brief primer to structured data.
What Is Structured Data and Why Is It Important?

Code that has been written in a predetermined format and is organised is referred to as “structured data.” Stated differently, data that has been “structured” Structured data comes in various forms that can all be applied in various contexts.
Strings of numbers and/or letters with a distinct pattern make up structured data. Its ease of entry, storage, querying, and management is crucial. All information that doesn’t fit neatly into a category, such as emails, blog posts, videos, photos, and web pages, is referred to as unstructured data.
One typical source of organised data is databases. Data in certain database fields is often managed and organised using Structured Query Language (SQL). The ability to query this structured data then makes it simple to locate specific data that is kept in the database, such as a client’s phone number or address.
Why Use Structured Data on the Web?
This article’s main topic, structured data on the web, is typically discussed in terms of search engine optimisation. The likelihood that your content will be seen by the intended audience is increased when pages and posts with structured data score well for relevant keywords in search results.
Additionally, it will enhance the appearance of your search results snippets, adding additional details about your material. This will raise your click-through rate by assisting users in determining whether your content is pertinent to their search queries.
How Does Structured Data Work on your Website?
Pages need to be “marked up” with structured data in order for search engines to efficiently index your website content. Adding code to your website in a manner that search engines can read is known as “marking up.”
This code will “talk” to the search engines and inform them what each piece of content is about when they crawl your website. As a result, the additional code will give structured data to the crawlers in place of discovering unstructured material on a web page or blog post, assisting them in identifying and prioritising the content’s essential elements.
Your material will appear in search engine results “richer” if you mark it up with structured data, since it will be more pertinent to the audience’s search and more helpful and educational. This is the origin of the term “rich snippets,” or “rich results,” as they are currently called.
(Keep in mind that Google makes no assurances. Rich snippets may not be generated for your pages even if you add structured data to your website.
We now have a basic understanding of what structured data is, why it matters, and how it functions on the internet. We will then examine structured data’s support for SEO in further detail.
How Does Structured Data Support SEO?
Your website’s search engine rankings ought to improve if you use structured data on it. These improvements may vary based on what your website contains.
By giving your content the following properties, structured data can help and enhance your SEO:
- Rich Outcomes
- Improved outcomes
- Google Knowledge Graph
- AMP
- Let’s now take a closer look at each of these.
Rich Results
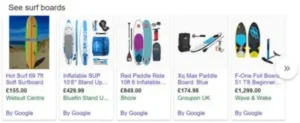
People prefer to read the synopsis of a book before making a purchase to learn more about it. Similar to rich results for webpages, rich results offer a thorough synopsis of a page or post’s content in search engine results. This enhances users’ online experience by letting them know if your site is what they’re seeking for or not. Additionally, it indicates that visitors to your website are drawn to your content and are interested in it, which lowers bounce rates and increases conversion.
Rich result features abound, offering summaries of web page material in a variety of formats. If you have added the right structured data to your site, Google will allow a set of rich results search capabilities for your page in the search results (We will describe how to achieve this further on in this post).
Two types of rich results search features exist:
- Content Type: A website’s search functionality is frequently reliant on its content. If you have a food blog, for instance, the search results for your pages can include information about ingredients, cooking hours, and recipes. On the other hand, Google search results may include event descriptions, locations, dates, hours, and costs if you are marketing events on your website.
- Features that can be applied to multiple types of content are called enhancements.
First, let’s talk about the features of the rich result for various forms of information.
Content Types

Rich results are generated depending on the code you have used automatically once you have marked up your site by providing the necessary structured data. Various rich formats are available on Google, and how they display results depends on the content.
The following list of frequently used content kinds includes the rich results search features that can be shown for each of them:
- Product: Present comprehensive product details, such as picture, cost, availability, and review scores.
- Article: Display rich result elements (title, text, and larger-than-thumbnail photos) in Google Search results.
- Book: Book purchases can be made straight from search results thanks to rich results.
- Course: Annotate a course with the name, a brief description, and the instructor’s contact information.
- Events: Make it easier for people to find out about your events by using Google Maps and Search.
- Podcast: Allow your podcasts to show up in Google along with descriptions of each individual episode and an embedded player.
- Recipe: Offer comprehensive results that include cooking and prep times, ingredients, and much more.
- Video: Display details about the video, including the length, upload date, thumbnail URL, and description.
As you can see, based on the kind of material on your website, many rich result formats are available for presentation. Next, let’s examine “enhanced” rich results, which have elements that are applicable to multiple types of information.
Enhancements
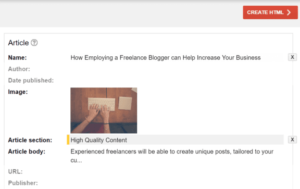
Features like enhanced rich results are applicable to multiple kinds of information. These are some of the improvements that can be used to show rich results for your content in Google Search.
- Carousel: To make your rich results eligible for Google’s list-like display feature Carousel (formerly known as Rich Cards), employ structured data. Carousel presently supports the following content types: article, recipe, film, and course.
- Choose the image that Google will use to represent your company’s logo in search results and the Knowledge Graph (more on this later).
- Corporate Content: Include your company’s contact information in the Google Knowledge Graph so that it shows up when a user types in the name of your business in the search box.
- Social Profile: To make your social media links appear in the Google Knowledge panel, use markup.
As was previously indicated, structured data can be utilised to mark up information to create “enriched results” in Google in addition to rich results. Let’s now examine enriched results and how they can improve the visibility of your content in search results.
Enriched Results
An enhanced search result is a more dynamic result type that allows for interaction. It is a relatively recent feature. This might appear as an engaging popup or another cutting-edge interactive element.
If you want your material to appear in an enriched result search experience, you will need to contribute structured data to your website pages. Enriched results are actually a subset of rich results. Content types like recipes, job postings, and events can all be tagged up to produce enriched results in Google.
Knowledge Graph Results
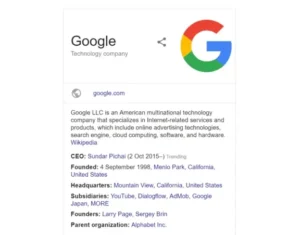
Structured data added to a business or brand’s website can have an impact on its Knowledge Graph. An informational synthesis from one or more webpages makes up a knowledge graph. A knowledge graph’s results can show the chosen site name, logo, social media profile links, and more.
AMP
Accelerated Mobile Pages is what AMP stands for. A Google-backed project called AMP was developed to assist publishers and developers in creating mobile-friendly pages that load quickly. You can build and validate AMP sites with the help of the AMP open-source library, which should help them rank higher in search results.
The content on AMP pages can be featured on Google mobile search as part of rich results and carousels by providing structured data to these pages.
By now, you should have a solid knowledge of how structured data can improve the way search engines display your website and individual pages. We’ll talk about adding structured data to your website next.
Schema.org
A collaborative initiative with Google, Microsoft, Yahoo, and Yandex was started in 2011 with the goal of developing a standardised list of entities for structured data on the internet. Schema.org, the web’s language for structured data, was born out of this.
Today, Schema.org is a vibrant community that develops, updates, and disseminates schemas for structured data on the web, in email correspondence, and on webpages. Rich experiences are provided by over 10 million websites and applications, including as Google, Microsoft, Pinterest, and many more, that employ structured data format to mark up their web pages and emails.
The vocabulary of Schema.org is compatible with RDFa, Microdata, and JSON-LD markups. Let’s examine each of these in more detail:
- Small-scale data Microdata is a type of semantic markup that integrates structured data into HTML content. It accomplishes this by naming the properties you wish to expose as structured using HTML tag attributes.
- RDFa: RDFa is an extension of HTML5 that facilitates the markup of items such as events, people, places, recipes, and reviews. It employs tag attributes (HTML5), just as RDFa, to give search engines an explanation of the information.
- JSON-LD – JavaScript notation is placed in a page head or body via a <script> tag, using an alternative markup methodology.
The main search engines use Schema.org, thus you should use it when adding structured data to your website. Google now advises using JSON-LD, which we shall examine in more depth below, when implementing markup on your website.
JSON-LD
As was already mentioned, one of Schema.org’s markups is JSON-LD, which is also, crucially, Google’s recommended approach. One way to use JSON to encode linked data is called JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data). JSON-LD has the advantage of being comparatively simple to read, write, and add to the pages of your website.
Every page displays a chunk of JavaScript code. This facilitates crawlers’ identification of the most important data presented in the markup. You are free to use any Schema.org schema in your JSON-LD block when adding JSON-LD markup to webpages.
How to Add Structured Data to Your Website
It is not necessary to have a lot of technical experience to add markup to your pages. Using Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper is the simplest choice. You can get guidance from this tool when writing code for various purposes.
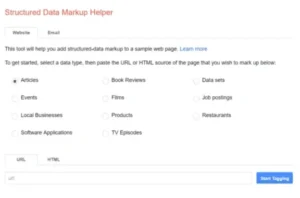
To begin marking up a page, just input its URL, choose the relevant data type (such as an article, event, book review, etc.), and click Start Tagging.
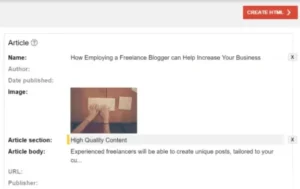
The page you want to add structured data to will open in Google. Now, you may mark (highlight) the content on the page that you want Google to find. For instance, you can tag a “article” with its name, author, publication date, image, and a tonne of other information.
Choose Create HTML once you have annotated every piece of information from your article that you want to see appear in your rich search results. For your article, Google will now show the right JSON-LD markup.
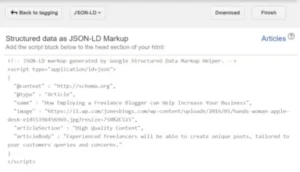
Next, on the relevant web page, add the JSON-LD script block beneath the <head> part of your HTML.
Additionally, Google offers comprehensive instructions on how to include markup into your website to produce rich results for various content kinds and upgrades. Yoast SEO and other WordPress SEO plugins can also be used to enhance SEO. Yoast SEO adds site information to the pages of your website using JSON-LD.
Markup Testing Tools
After adding structured data to your web pages, you can use a variety of tools to make sure your markup is accurate and functional.
Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool
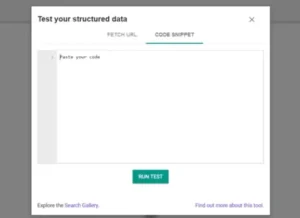
With Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool, you can verify that your markup is functioning properly by testing it. All you have to do is copy your code into the tool, and Google will test it, finding any mistakes or warnings.
Bing Markup Validator
Bing has a structured data testing tool of their own as well. You may test HTML Microdata, Microformats, RDFa, Schema.org, and OpenGraph with the Bing Markup Validator. Although using this service is free, you must first register for a Bing Webmaster Tools account.
Additionally, Bing offers a wealth of information on structured data, SEO, and website markup for their search engine.
Yandex Webmaster
An additional powerful structured data validator is Yandex Webmaster. You can use this tool to verify several microformats, such as RDF, Microdata, OpenGraph, and Schema.org.
Just input the URL of the webpage you want to check or the HTML code snippet to utilise Yandex Webmaster. Next, the validator will examine your webpage’s semantic markup to ensure that indexing bots can retrieve all the information you wish to show up in search engine results.
Final Thoughts
As you can see, a crucial component of any website is structured data. However, because of its complexity, it is frequently disregarded or neglected. Now that you have a solid knowledge of how structured data can help enhance the search engine results for your website, it’s time to make sure that all of your pages and articles are appropriately marked up. Are you prepared to begin?
Do you have any inquiries about incorporating structured data into your website? If so, don’t hesitate to ask questions in the section below.
GET MORE INFORMATION VISITON………..Couponsberg.com
FAQs : Structured Data