SEO Audit : A thorough assessment of a website’s search engine optimisation effectiveness is called an SEO audit. Finding the site’s advantages, disadvantages, and areas for development is the main objective of an SEO audit, which aims to increase the website’s exposure in search engine results pages (SERPs). An SEO audit assists in making sure that a website complies with best practices and is optimised to draw in and keep organic traffic by methodically examining different parts of the site.
What Is an SEO Audit?
The practice of assessing how well your website is search engine optimised is called an SEO audit. It finds mistakes that could hinder your website’s search engine ranking as well as chances to increase your online presence.
Typically, an SEO audit looks at things like:
- Crawlability and indexing
- User encounter
- Site architecture Benchmarking against competitors
- Research on keywords
- Page-by-page SEO
- Profile of backlinks
It functions as a website’s general “health check.”
SEO Audit Tools
Hard data regarding your website’s traffic, backlink profile, and technical health (as well as those of your competitors) is the foundation of any successful SEO website audit.
The two most crucial resources that might assist you with that are:
- Google Search Console is a collection of dashboards and reports that let you keep an eye on and troubleshoot any problems with your website showing up on Google.
- Semrush is an all-in-one SEO toolkit that helps you optimise your website in all the important SEO areas and offers a thorough analysis of its performance.
In the following sections, we’ll examine how to use these tools to conduct an SEO audit in more detail.
How to Do An SEO Audit
1. Check for Indexing Issues
Google’s database does not contain pages that are not indexed. They are not ranked by Google.
Use Google Search Console to immediately check for problems to determine if your pages have been indexed.
Navigate to the “Pages” report located in the “Index” part of the menu on the left. This is a graph showing every page according to its indexing status.
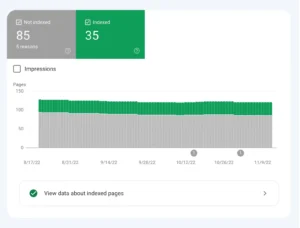
A list of the reasons why pages haven’t been indexed is below.
Go over each of the reasons stated one by one. Examine the pages that correspond with these explanations.
Recall that just the pages you wish to appear high up in search results need to be indexed. Therefore, having some URLs that are not indexed is quite common.
Here are a few instances of URLs that are exempt from indexing requirements:
- Redirected pages
- Pages for administrators
- Different pages using the official tags
- Pages for feeds
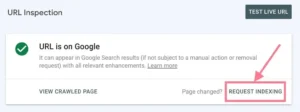
If you discover a page that ought to be indexed but isn’t, take Google’s instructions to rectify the problem. Press the “Validate Fix” button when finished.
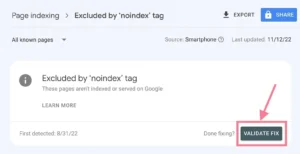
As an alternative, you may simply copy and paste a specific URL into the Google Search Console dashboard’s top search field.
See the status of the URL. By selecting the “Request Indexing” link, you may also ask Google to index the URL.
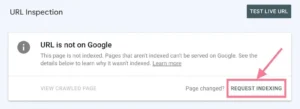
You can resubmit the request for indexing if the page has undergone significant alteration. in spite of the page’s prior indexing.
Using Site Audit, you can find 140 other technical SEO issues as well as indexing issues.
Navigate your website and choose the “Issues” section.
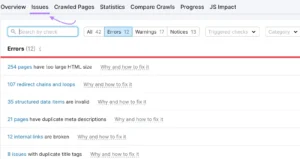
These are all the mistakes, alerts, and notices impeding the SEO performance of your website.
Now, to view only indexing concerns, choose “Indexability” from the “Category” dropdown menu.

2. Check for Duplicate Versions of Your Site
Making ensuring that Google is only indexing one version of your website is crucial.
Depending on whether HTTPS is used by your website and if the domain contains WWW, different URL variants may be used for it.
These are all distinct versions of the website to a search engine:
/[www.yoursite.com]
/* yoursite.com
/[www.yoursite.com/]
/*yoursite.com
Multiple URL variations for your website might lead to various problems with crawling, indexing, and ranking. In particular, Google will consider them to be duplicates.
Additionally, having different versions of your website might lower PageRank, which can hurt your search engine rankings.
This is fairly simple to verify:
- Simply load your website in all of its versions into a web browser.
- The desired version should be immediately forwarded for you.
For instance, if you type any other version of the URL into your browser and your preferred version is https://yoursite.com, you should be forwarded to it.
If your website is available in more than one version, utilise a 301 redirect for those versions.
3. Run a Site Crawl
A crawl-based SEO assessment performs well.
This implies that you ought to be able to mimic how Google scans your webpages. and view every problem associated with those pages as if they were seen by Google.
You’ll need a website SEO auditing tool like Site Audit to accomplish that.
You will first organise the audit and create a project.
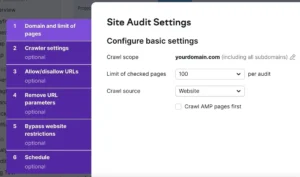
This stage involves multiple setups. To assist you in navigating it, you can refer to this tutorial.
After everything is ready, press the “Start Site Audit” button.
It can take some time to complete, depending on the amount of pages that are being crawled. You will receive an email notifying you when it’s finished.
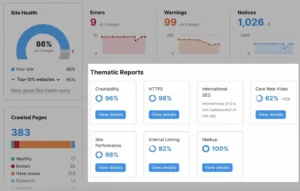
This is how the audit dashboard appears:
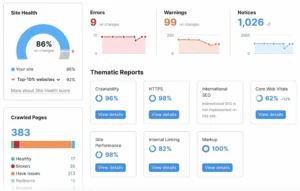
The Site Health score is the primary measure that warrants your attention.
It is a general measure of your website’s SEO health based on the quantity and severity of problems discovered.
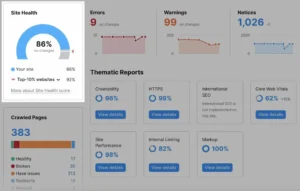
After that, the problems will be categorised into three groups:
- Notices & Warnings Errors
These will assist you in setting repair priorities. Prioritise fixing errors, followed by warnings and notices.
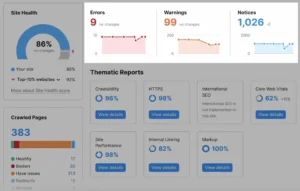
Additionally, “Thematic Reports” are available to assist you in delving deeper into a number of technical SEO topics:
We’ll dive deeper into some of these in the following steps.
However, the main purpose of the Site Audit tool is to help you see all the issues in one place.
To do this, click on the “Issues” tab:
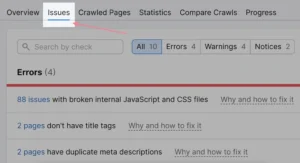
An exhaustive list of all the problems is available. Start by going over each one individually and addressing it.
To view a list of all the URLs that are impacted, click each issue.
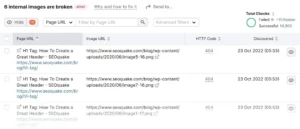
Here are some scenarios of problems you can run into:
- Crawlability problems: for example, certain pages returned a 5xx status code.
- Redirect problems: for example, some of your redirects are repeated
- Problems with your sitemap, such as the discovery of some inaccurate pages
- HTTPS problems include the fact that HTTPS pages connect to HTTP pages.
- Internal link problems: for example, a broken or non-functional internal link
- On-page SEO problems: for example, several of your pages lack title tags.
- Markup problems: some structured data markup, for example, does not adhere to Google’s standards.
- Performance problems: some webpages take a long time to load
Fixing some of these problems is rather simple. A more intricate solution might be needed for some.
For each problem, the tool provides a brief “how to” tutorial and an explanation, in case you’re not sure where to begin.
Simply select “Why and how to fix it.”
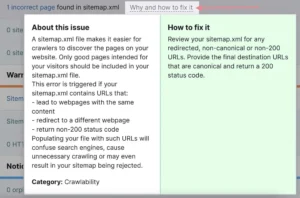
Side note:
Use Site Audit now; you don’t need to wait until your next SEO audit. Utilise the Site Audit tool frequently to monitor your development and find any new problems that may have emerged since the last crawl. Also, have a look at some of our advice on corporate SEO audits for people with bigger websites.
4. Check for Manual Actions
Your website can be subject to a manual action from Google if it breaches its spam standards.
When Google takes a manual action, your site’s rankings will suffer until the action is reversed. This can apply to the entire website or just specific pages.
You might have received a manual action for a number of reasons, such as:
- Stuffing keywords
- Links that aren’t natural (from and to your site)
- Different types of spam
- Thin material with minimal or no value addition
If you’ve received a manual action, you may verify it in Google Search Console.
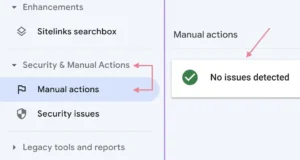
There is a “Manual actions” link under the “Security and Manual Actions” part of the menu on the left-hand side.
When you click it, a page with the status will load.
Ideally, a check mark with a green colour appears, indicating that no problems have been found.
In the event that your website is the subject of a manual action, you must resolve the matter and request reconsideration. For further information, see Google’s Manual Actions guide.
For instance, if purchasing backlinks resulted in a manual action (“Unnatural links to your site”), you will need to remove those backlinks either disavowing them or contacting the webmasters.
5. Check for Mobile-Friendliness Issues
In the mobile-first era we live in, you are probably not prioritising your user experience if your website isn’t optimised for mobile devices.
One of Google’s primary Page Experience indications is mobile friendliness.
Since 2015, in fact, it has been a component in rankings. which implies that it may have a direct impact on how well you rank in search results.
The Google Search Console’s Mobile Usability report allows you to look for any problems.
Simply select “Mobile Usability” from the menu on the left under “Experience.”
This is a brief summary of how usable your pages are over time:

The report will also provide a list of all the problems with mobile friendliness.
Similar to this
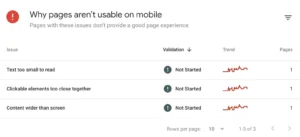
To view all the pages impacted by a certain issue, expand each one.
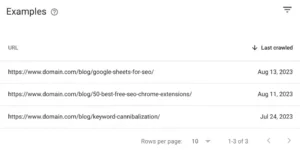
To resolve the problems, according to the guidelines provided in Google’s Search Console Help centre.
After the problem has been repaired, you may verify the change to ensure Google reevaluates the page and verifies that the problem has been fixed.
6. Analyze Your Site’s Speed
Now more than ever, it is critical that your website loads quickly. For a very long time, page speed has also been a ranking component. Consequently, it may raise your Google ranking.
Furthermore, it is a crucial component of the user experience. Based on user behaviour, evidence indicates that a slower loading page increases the likelihood that a user will leave the website.

Go to the “Site Performance” report from your Site Audit dashboard to see how quickly your site loads.
Here:
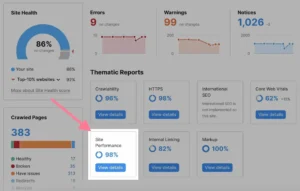
This is where a list of all the problems affecting the loading speed of your website appears.
Click “Why and how to fix it” to find out more about a problem and how to solve it.
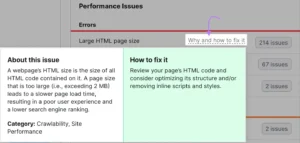
Take care of as many problems as you can. Additionally, your website’s speed and ranks ought to increase.
7. Analyze Your Core Web Vitals
Three new measures pertaining to page performance and user experience were released by Google in 2020.
- The longest time it takes to load the greatest portion of the page is measured by the greatest Contentful Paint (LCP).
- The term “First Input Delay” (FID) refers to the time lag that occurs between a user’s initial interaction with a page and the browser’s response.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): gauges both the degree to which the user’s view of the page changes and its visual stability.
They’re referred to as Core Web Vitals together.

Examining these metrics for your important pages should undoubtedly be a part of any SEO site audit, as Core Web Vitals are a ranking consideration.
Once more, Google Search Console proves to be helpful.
Navigate to the “Experience” area on the left menu and select the “Core Web Vitals” report.
Reports labelled “Desktop” and “Mobile” will appear, outlining every problem along with the pages that are impacted.
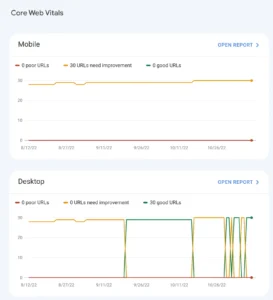
You’ll get thorough insights into any Core Web Vitals problems your website might be experiencing with these reports.
The programme makes a distinction between pages that require minor adjustments and those with serious problems (also known as “poor URLs”).
Examine the problems and adhere to the recommendations for resolving them.
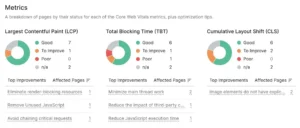
Additionally, Site Audit includes a specific Core Web Vitals analysis.
Simply select the “Core Web Vitals” dashboard widget.

Moreover, a breakdown of every parameter will be shown.
Similar to this
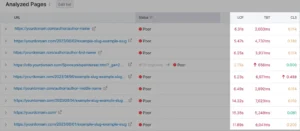
You will find a table titled “Analysed Pages” if you scroll below.
Take a look at all of the stats at the single-page level and monitor your development over time.
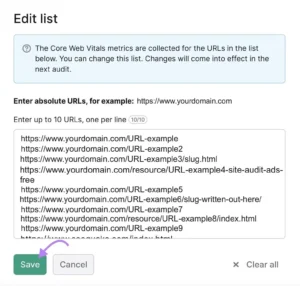
Additionally, you may manually choose ten URLs to have Core Web Vitals concerns checked. Simply select “Edit list” from the menu.
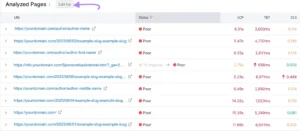
The list can then be edited as desired. Next, select “Save.”
8. Analyze Your Internal Links
For three reasons, internal links are an essential component of SEO.
They facilitate webpage crawling by search engines.
They facilitate users’ navigation of your website.
They assist you in directing “authority” or “link juice,” also known as link equity, to the most crucial pages.
Site Audit has a report specifically on problems with internal linking. Select “Internal Linking” from the “Thematic Reports” list:
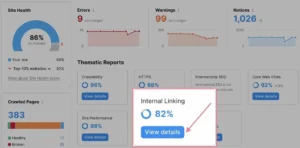
You’ll receive a list of problems with internal links along with instructions on how to resolve them.
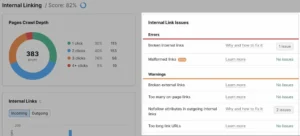
A helpful summary of your pages based on Internal LinkRank (ILR), a metric that assesses how well a page is interlinked, will also be provided by the report.
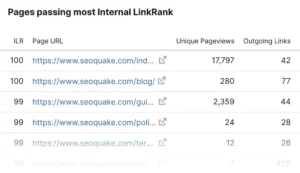
By going over each category, you’ll be able to distinguish between two kinds of pages:
- Not many internal links are pointing to important pages, thus you should point additional internal connections to them.
- Good internal linking reciprocity (ILR) pages (so you may use them to distribute link equity to other pages)
9. Check Your Organic Traffic
The term “organic traffic” refers to users who find your website through clicking on “organic,” or free, search results.
When it comes to SEO, this is among the most significant markers of your website’s performance.
Go to Google Search Console and select the “Search results” report from the “Performance” section of the menu to view your organic traffic.
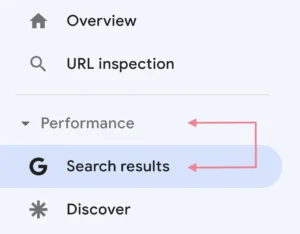
The report has four primary metrics.
In this case, “Total clicks”—the number of times a person clicked through to your website during the allotted time—will be the most interesting metric.
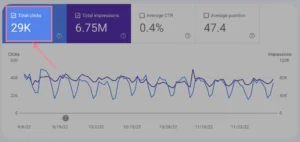
To view the data you require, you can configure the report in a variety of ways.
As an illustration, results can be seen by devices, nations, pages, and queries:
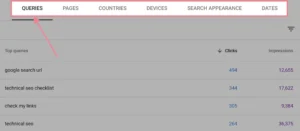
You may learn a great deal about the organic traffic to your website from these statistics. and assist you in setting benchmarks and monitoring your advancement
10. Benchmark Against Your Competitors
An effective SEO audit ought to assist you in assessing your position in relation to your rivals.
Using Domain Overview is a fantastic place to start.
First, click “Search:” after entering your domain and country.
Next, select the option labelled “Compare domains.”
You can choose up to four rival domains here. Select the suggested domains by the tool if you are unsure of who your primary rivals are.
Next, select “Compare.”
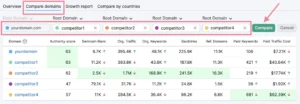
You will receive a reliable comparison of the important metrics for the chosen domains from the tool. These will provide you with a clear picture of your areas of strength and weakness.
Pay attention to the following parameters for the best overview:
- Authority Score: a measurement of the domain’s general quality ranging from 1 to 100 (based on search traffic, backlinks, and other variables)
- Organic Traffic: The volume of organic traffic that the website gets
- Organic Keywords: displays the number of terms for which the website ranks
- Referring Domains: indicates the total number of domains that point to the examined domain. This gives a more accurate comparison than the total number of backlinks.
We’ll look at ways to advance competitor research in the next two steps. Additionally, make the most of the backlink data and keywords of your rivals.
11. Find Keywords You’re Missing Out On
Examining the keywords that your rivals target is a fantastic opportunity provided by SEO audits. as well as whether there are any opportunities you’re overlooking.
Enter your domain and up to four rival domains when the Keyword Gap tool opens. Next, select “Compare.”

The keyword sets that the analysed domains are ranking for will be compared by the programme.
Look closely at the “Missing” and “Weak” tabs after swiping down to the list of keywords:
- Absent: terms that you don’t rank for but your rivals do
- Weak: keywords that your rivals rank higher for than you
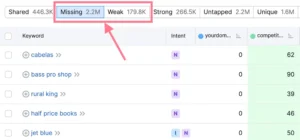
You might find some previously undiscovered hidden keyword opportunities in the list.
12. Find Missed Backlink Opportunities
You may use the Backlink Gap tool to uncover backlink chances in a similar way to how you would use the Keyword Gap tool to find amazing keyword prospects.
Simply insert the domains of up to four rivals together with your own. Next, select “Find prospects.”
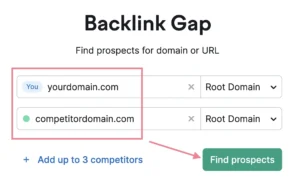
A list of domains that connect to your rivals but not to you will be displayed by the tool:
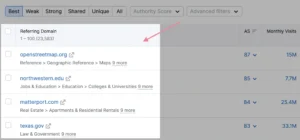
Since these domains already link to related websites (your competitors), there is a significantly higher chance that they will link to your website.
Select the arrow adjacent to the figure that represents the quantity of backlinks originating from a specific domain.
By doing this, the view is expanded to include particular pages that connect to your rivals. in addition to the target URLs and anchor text.
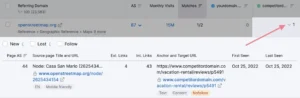
You can now attempt to create duplicate backlinks.
Click the “Start outreach” button located in the upper-right corner after selecting the ones that pertain to your website.
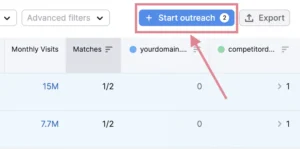
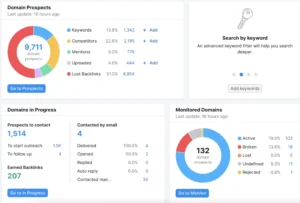
The chosen leads will then be forwarded to the Link Building tool, where you can create a new project just for your domain.
The instrument will support you in:
Locate potential backlinks from a range of sources.
Speak with the domain owners and request backlinks from them.
Monitor the success of your outreach initiatives.
13. Audit and Improve Your Top Pages
Using a general site crawl, you can identify any technical problems with your entire website.
But it’s also a good idea to examine individual pages more closely (particularly the ones that are most significant to you), assess how well they operate, and identify areas for improvement.
In essence, an assessment of on-page SEO.
You can do it with the aid of a useful tool called On Page SEO Checker.
After setting up the project, add the pages and their intended keywords.
You have the option to manually enter the pages and keywords or let the programme to locate them for you.
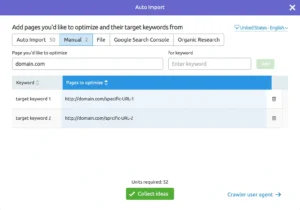
It’s not necessary for you to review every page. Rather, pay attention to those who:
- Generate the greatest number of conversions
- Concentrate on the terms that are most crucial to your company.
The tool will assess your data against that of your top-ranking competitors and offer helpful advice on how to raise your ranks in a number of on-page SEO audit categories.

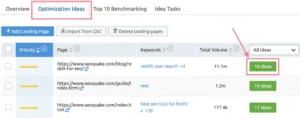
To view the suggestions for a given page, select the “Optimisation Ideas” tab. And select the green button next to the page’s URL that displays the number of ideas:
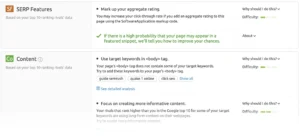
Below is a comprehensive summary of all the recommendations, complete with levels of difficulty and advice:
14. Monitor Your Rankings
One of the greatest methods to always monitor how well your website is performing in organic search results is to use a rank tracking tool.
With these tools, you can:
- Monitor the positions of your website for important keywords.
- Examine the variations in search engine results page (SERP) ranks across different regions.
- Compare your position to that of your rivals.
- Receive notifications of any significant changes to your website’s rankings.
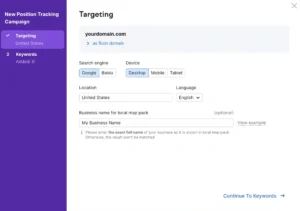
Open Semrush’s Position Tracking tool and enter your domain to begin rank tracking.
You may configure the search engine, device, and location parameters for your tracking under the basic settings.
You will then be asked to input the terms that you wish to monitor.
You have three options: apply Semrush’s suggestions, import data from an external file, or enter data manually.
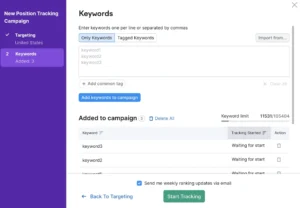
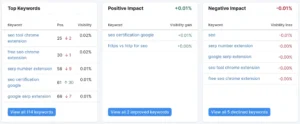
You can keep an eye on all of the changes to your ranks in one location with your newly formed position tracking project.
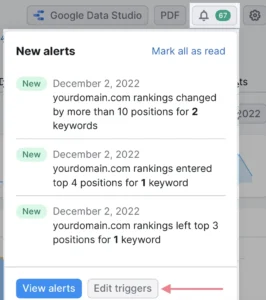
Click the small bell icon in the upper right corner to configure alerts.
Here, you may configure different triggers (such a keyword showing up in the top ten results) and receive immediate email notifications when these changes occur.
READ MORE INFORMATION ………..Couponsberg.com
FAQs: About SEO Audit
***
