Emerging Blockchain Technology : As the original cryptocurrency, bitcoin is well known to most people. Its price has increased by about 1700% since the start of the year. People are naturally curious. However, blockchain technology, the underlying technology, is what tech experts are more interested in.
Blockchain might have an impact on many sectors of the economy. It has the potential to alter how we do business. It’s referred to as “Internet 3.0.” Thus, many in the web hosting and e-commerce industries are considering the possibilities of this technology.
Numerous businesses are developing apps and web hosting services on different blockchains. However, it’s crucial to comprehend the fundamentals of blockchain technology, applications, and history before getting started with blockchain hosting. It will provide you with some background information so you can see the potential it has for your web hosting company.
The Beginning of Blockchain
As the original cryptocurrency, bitcoin is well known to most people. Its price has increased by about 1700% since the start of the year. People are naturally curious. However, blockchain technology, the underlying technology, is what tech experts are more interested in.
Blockchain might have an impact on many sectors of the economy. It has the potential to alter how we do business. It’s referred to as “Internet 3.0.” Thus, many in the web hosting and e-commerce industries are considering the possibilities of this technology.
Numerous businesses are developing apps and web hosting services on different blockchains. However, it’s crucial to comprehend the fundamentals of blockchain technology, applications, and history before getting started with blockchain hosting. It will provide you with some background information so you can see the potential it has for your web hosting company.
Among the topics covered in this guide are:
The Beginning of Blockchain
Blockchain has a mysterious beginning. A white paper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” was released in 2008 by a person going by the name of Satoshi Nakamoto. It’s still unclear who Satoshi Nakamoto really is. The blockchain technology and bitcoin were covered in the white paper. With Nakamoto’s assistance, a group of programmers created the original bitcoin blockchain by 2009. Nakamoto was exclusively communicated with by the community via emails and online discussion boards.
The financial crisis piqued the attention of early adopters of bitcoin in the technology. Their goal was to create a system that wouldn’t need rules. It would be an unrestricted system for value exchange. However, the adopters soon began to realise the possibilities. The community continued to expand as news spread that bitcoin was a novel method of payment and that users could earn bitcoins by mining or contributing to the upkeep of the blockchain. The price of Bitcoin began to rise.
Bitcoin has grown astronomically in 2017. With a market valuation of more than $160 billion, the price of bitcoin nearly hit $20,000. Even the most devoted fans of bitcoin have been taken aback by its explosive surge.
The Blockchain Technology
The blockchain technology involves intricate mathematics. However, the blockchain principle is simple. Fundamentally, blockchain consists of a distributed digital ledger that is updated.
The majority of businesses nowadays keep a database of their transactions. Current databases function as ledgers. Nonetheless, the integrity of such transactions must be upheld by the business that owns the database. We rely on these businesses to maintain accurate records whenever there is a value exchange.
The organisations that monitor these transactions can be e-commerce platforms such as Amazon or eBay, or they can be financial organisations such as banks or credit card companies. The transactions are guaranteed by third parties when we purchase a goods from a store or online.
This implies that a third party is required for any transaction. This is not a recent occurrence. To ensure honest transactions in the past, individuals relied on village elders or other methods rather than banks.
Blockchain has the power to alter this transaction’s dynamics. Under the existing system, a third party provides the trust factor by validating identity, transaction amount, and other details when two persons trade value (goods, services, or anything else).
A blockchain eliminates the requirement for a reliable third party. Value exchanged between two parties is digitally recorded on the ledger through a distributed network.
This ledger’s records cannot be altered. It implies that no one can alter the ledger record by returning. Thus, the third party is not required to monitor the communication between the two parties. We refer to them as trustless transactions.
Through the use of encryption, blockchain technology facilitates trustless transactions. Users broadcast transactions in a blockchain network. Volunteers known as “miners” pick up and gather these transactions. Original blockchain copies are in the hands of miners. The gathered transactions are bundled together into a block after a predetermined period of time. The block is then included in the blockchain.
On the other hand, the block addition follows a procedure. Every block has a computationally challenging problem assigned to it. The miners then compete with one another to find a solution. The puzzle is designed in a way that makes it easy to check the solution even if solving it requires processing resources. The block is added by the miner who solves the puzzle first. Tokens from the blockchain are awarded to the miners who successfully secure the privilege. Users are encouraged to volunteer as miners via this.
Cryptographic hashes are used to link the blocks together. Because of this, the hashes will alter and reveal the fraud if someone modifies any one of the blocks, even slightly. A user can easily discard a corrupted blockchain and obtain a copy of the genuine blockchain from another person if they come across one. Because of its immutability, the blockchain is protected from manipulation.
Various Blockchains
There are numerous cryptocurrencies and blockchains, even if bitcoin is the most well-known. Because it is the blockchain with the smart contract, Ethereum is important. On blockchains, smart contracts are executable codes. These scripts work under the correct conditions. For instance, a smart contract can be used to pay an employee. The smart contract will start a payment process at the conclusion of each month. Other cryptocurrencies include Monero, Zcash, Ripple, Litecoin, and more. Every day, new blockchains are formed. Businesses are experimenting with private blockchains as well.
Applications of Blockchain
The applications of blockchain technology are extensive. Here are some illustrations to help you understand the importance of this technology:
- It can be used by banks and financial institutions to enhance their procedures. Insurance policies and mortgages can be kept on blockchains.
- Blockchain technology can be used to store medical records. Drugs can also be monitored using it. This can stop medications from being misused or used illegally.
- It can be difficult for the network to maintain Internet of Things (IoT). Blockchain technology can supply the infrastructure required to meet this technology’s requirements.
- Blockchain can be used by governments to keep land records up to date. It can be applied as a voting mechanism.
- DNS can be maintained on blockchains by web hosting companies.
Where Are We Going with This?
- According to a research by Allied industry Research, the growing use of blockchain technology across a range of industries is predicted to propel the blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) industry, which is projected to reach $15.4 billion by 2026.
- 84% of businesses, according to a PwC poll, are actively using blockchain technology in some capacity, demonstrating the technology’s rising popularity and uptake.
- According to a MarketsandMarkets analysis, growing industry use of blockchain technology is predicted to propel the worldwide blockchain market from $3 billion in 2020 to $39.7 billion by 2025.
- According to a Frost & Sullivan analysis, the utilisation of blockchain technology in healthcare is anticipated to reach $1.7 billion by 2026. The requirement for transparent and safe patient data handling is what motivates this.
- Based on a research by IDC, the blockchain market in the US is anticipated to grow to $41 billion by 2025, mostly due to growing use in the supply chain, healthcare, and financial services sectors.
- The possible influence of this technology is demonstrated by the fact that, in a KPMG survey, 48% of executives said they thought blockchain would revolutionise the way they do business in the next three years.
- Blockchain technology has the potential to save global investment banks up to $12 billion annually by lowering infrastructure costs and boosting productivity, according to an analysis by Accenture.
- According to a survey by Meticulous Research, the food and beverage industry is predicted to have a CAGR of 48.1% in the usage of blockchain technology between 2020 and 2025.
- According to an IBM survey, nine out of ten government agencies intend to invest in blockchain technology by 2021, demonstrating the public sector’s rising interest in and use of this technology.
- A report projects that the Asia-Pacific blockchain market will expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 87.6% between 2020 and 2027, mostly due to growing adoption in nations like China, Japan, and India.
Hosting a DNS Domain on Blockchain
The Ethereum blockchain is hosting the URL docs.ens.domains [https://docs.ens.domains/en/latest/]. On the Ethereum blockchain, DNS domain hosting is supported in an experimental manner. Still, it presents a compelling use case for blockchain technology and web hosting.

Ethereum Name Service, or ENS, is used in the experimental project to create the DNS service. Nameservers use DNS to respond to queries authoritatively and to identify other nameservers by name. The nameserver is consulted when a user is attempting to fix a problem. The nameserver moves on to the next one if it is unable to resolve the queries.
Since Ethereum is native, ENS is included. Its main objective is to resolve names that are “human-readable.” The goals of DNS and ENS are similar. However, the ENS maintains a central database that links resolvers to domain names. Every domain owner has the ability to modify the resolver address. The user utilises the registry to locate the resolver—which can find the response to the query or question—in order to look up domain information. ENS lacks zones, but DNS uses the idea of zones to function.
For the current DNS hierarchy, one ENS resolver could be used. However, the issue of DNS ownership proof will arise, raising the question of who will have the authority to make registry changes. The experimental solution uses a method that lets anyone host any collection of domains and deploy their own ENS resolver and registry.
Let’s use an illustration. If your domain, “www.onlyawebsite.com,” has an ENS registry set up with the address 0x55555555. You instruct the registrar to set “55555555.ns1.ens.domans” as the nameserver for your “www.onlyawebsite.com.” Now, doing a search for “www.onlyawebiste.com” will start the subsequent procedure:
- “www.onlyawebsite.com NS 55555555.ns1.ens.domains” is found using recursive resolution.
- The inquiry is received by “ns1.ens.domain,” the gateway server. After searching for “www.onlyawebsite.com,” it receives the answer.
- The ENS registry is queried by the gateway server.
- The resolver is questioned by the gateway server for the zonefile for “www.onlyawebsite.com.” It unpacks the data in memory after retrieving the DNS zonefile information in a condensed binary format.
- The unpacked zonefile can now be used by the getaways to respond to the initial question.
DNS domain hosting on ENS is currently in its testing phase. Situations involving production levels shouldn’t use it. However, it does give you a sense of the extent of integration that blockchain technology can accomplish.
Blockchain Hosting and Storage
Other businesses are prioritising blockchain technology. Here are a few of them:
Shift presents itself as a decentralised online platform. Peer-to-peer data storage and smooth monetization are made possible by the platform.
HostCoin

HostCoin prides itself on being the first blockchain-based web hosting provider. Awaiting its first coin offering (ICO) is the situation. HostCoin aims to improve security by using blockchain technology for hosting.
Sia
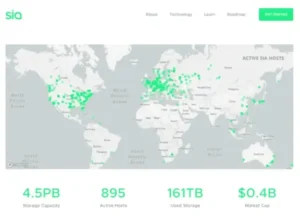
Sia is a blockchain-secured decentralised storage platform. Repetitive, inexpensive, and private. It makes use of global hard drive capacity that is not being used to provide a more dependable and affordable data storage marketplace than typical cloud storage providers.
Storj
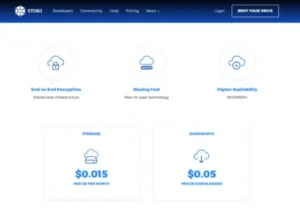
Distributed object storage that is end-to-end encrypted and restricts access to your data only. Blockchain payments are the engine. Buy only what you actually use. Both setup and usage expenses are waived.
SONM

The Ethereum blockchain powers SONM, a fog supercomputer that can operate anywhere. Customers gain from the cost-effectiveness, security, and scalability of SONM fog computing over centralised cloud services. Since the data is encrypted, decentralised, and saved on miners’ computers in the fog, neither infrastructure nor staff are required.
Golem

Golem is an accessible, decentralised, global supercomputer that is open source. Golem allows any user, from a single PC owner to a huge data centre, to share resources.
MadeSafe

The SAFE Network is a new independent and decentralised data network that MaidSafe is developing. The bandwidth, processing power, and unused hard drive space of its users make up the network. To mention a few of its capabilities, the SAFE Network will offer storage, peer-to-peer communication, transactions, internet connectivity, and a large selection of apps.
Filecoin

A cryptocurrency and storage network powered by blockchain. Data encrypted from end to end and kept in safe sections. Turn your unused storage into a source of income by mining Filecoin. Get compensated for completing storage requests on the Filecoin market by using the Filecoin mining software.
GET MORE INFORMATION VISIT ON…………….Couponsberg.com
FAQs : Emerging Blockchain Technology
1. What is blockchain technology?
Answer: Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers in such a way that the registered transactions cannot be altered retroactively. This technology ensures transparency, security, and immutability of data. It underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and has potential applications in various sectors including finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more.
2. How does blockchain work?
Answer: Blockchain works by recording transactions in blocks, which are then linked together in a chain. Each block contains a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block. This structure ensures that once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be changed without altering all subsequent blocks, providing a secure and immutable record of all transactions.
3. What are the different types of blockchain?
Answer: There are primarily three types of blockchain:
- Public Blockchains: These are open to anyone and are fully decentralized (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum).
- Private Blockchains: These are restricted to a specific organization or group and are more centralized.
- Consortium Blockchains: These are semi-decentralized and controlled by a group of organizations rather than a single entity (e.g., Hyperledger).
4. What are smart contracts and how do they work?
Answer: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute and enforce the terms of an agreement when predefined conditions are met. Smart contracts run on blockchain networks, ensuring transparency, immutability, and automation of processes without the need for intermediaries.
5. What are some potential applications of blockchain technology?
Answer: Blockchain technology has numerous potential applications across various industries, including:
- Finance: Cryptocurrencies, cross-border payments, and transparent auditing.
- Supply Chain: Tracking the origin and journey of goods to ensure authenticity and reduce fraud.
- Healthcare: Secure and efficient management of patient records and data sharing.
- Voting Systems: Ensuring transparent and tamper-proof elections.
- Real Estate: Simplifying property transactions and ownership records.
6. What are the main challenges facing blockchain adoption?
Answer: Despite its potential, blockchain adoption faces several challenges, including:
- Scalability: Difficulty in handling a large number of transactions quickly and efficiently.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear regulations and guidelines in many regions.
- Interoperability: Challenges in integrating different blockchain networks and systems.
- Energy Consumption: High energy usage, especially in proof-of-work systems like Bitcoin.
- Security: Although secure, blockchains can still be vulnerable to certain types of attacks, such as 51% attacks.
